The credit to debt ratio is an important financial metric that measures an individual’s or a company’s ability to manage and repay their debts. It is also known as the debt-to-income ratio or the debt ratio. Understanding this ratio is crucial for lenders, as it helps them assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
Calculating the credit to debt ratio involves comparing the total amount of debt owed to the total amount of available credit or income. This ratio is expressed as a percentage and can be calculated using the following formula:
Credit to Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Available Credit or Income
To illustrate this calculation, let’s consider an example. Suppose an individual has a total debt of $10,000, including credit card debt, student loans, and a mortgage. Their total available credit or income is $50,000. The credit to debt ratio would be calculated as follows:
| Total Debt | Total Available Credit | Credit to Debt Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | $50,000 | 20% |
In this example, the individual’s credit to debt ratio is 20%. This means that they have used 20% of their available credit or income to repay their debts. A lower ratio indicates a better financial position, as it demonstrates the ability to manage and repay debts effectively.
What is credit to debt ratio?
The credit to debt ratio is calculated by dividing the total debt by the total available credit. For example, if an individual has a total debt of $10,000 and a total available credit of $20,000, their credit to debt ratio would be 0.5 or 50%. A lower ratio indicates a lower level of debt relative to available credit, which is generally seen as favorable.
In order to maintain a healthy credit to debt ratio, individuals should try to keep their debt levels low compared to their available credit. This can be achieved by making regular payments on time and avoiding maxing out credit cards or taking on excessive amounts of debt. A high credit to debt ratio can make it more difficult to obtain credit in the future and can also negatively impact credit scores.
Key points:
- The credit to debt ratio measures the proportion of total debt used in relation to available credit.
- A lower ratio is generally seen as favorable and indicates a lower level of debt relative to available credit.
- Maintaining a healthy credit to debt ratio involves keeping debt levels low and making regular payments on time.
Why is credit to debt ratio important?
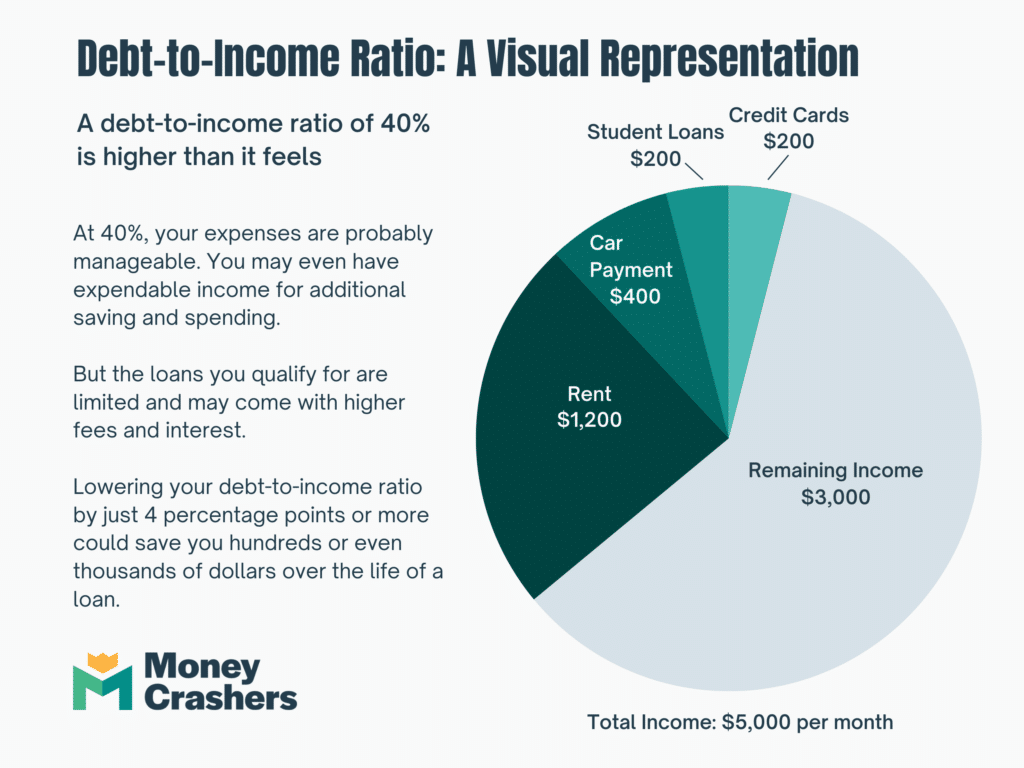
There are several reasons why the credit to debt ratio is important:
- Lender perspective: Lenders use the credit to debt ratio as an indicator of a borrower’s ability to manage their debt. A higher ratio suggests that a person is using their credit responsibly and can handle additional credit, making them more likely to be approved for a loan or credit card.
- Financial health: Monitoring and maintaining a healthy credit to debt ratio is crucial for one’s overall financial health. A high ratio indicates that a person is effectively managing their debt and is less likely to experience financial stress. It also shows that an individual is not heavily reliant on credit to meet their financial obligations.
- Impact on credit score: The credit to debt ratio is a significant factor in determining an individual’s credit score. Credit utilization, which is the ratio of credit used to credit available, accounts for about 30% of a person’s FICO credit score. A lower credit to debt ratio can positively impact credit scores, leading to better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased borrowing power.
An individual should strive to maintain a credit to debt ratio below 30% to be considered a favorable borrower in the eyes of lenders.
Calculating Credit to Debt Ratio in Real Estate

To calculate the credit to debt ratio in real estate, you need to consider both the property’s outstanding debt and its available credit. The formula is:
Credit to Debt Ratio = Total Outstanding Debt / Total Available Credit
In real estate, the total outstanding debt refers to the amount of money owed on the property, which includes any mortgages, loans, or other debts related to the property. The total available credit is the maximum amount of credit that can be accessed, such as a line of credit or the property’s appraised value.
Once you have the total outstanding debt and the total available credit, you can calculate the credit to debt ratio by dividing the total outstanding debt by the total available credit. The resulting ratio will give you a percentage that indicates the level of debt relative to the available credit. A higher ratio signifies a higher level of debt and may indicate a higher risk for lenders or investors.
Understanding the components of real estate
Land: Land is one of the essential components of real estate. It refers to the earth’s surface, including everything attached to it naturally, such as trees and water bodies. Land can be further categorized into different types, such as residential, commercial, or agricultural land.
Buildings: Buildings are another critical component of real estate. They refer to any structures or constructions built on the land. Buildings can include residential houses, commercial buildings, industrial warehouses, or even public facilities like schools or hospitals.
Improvements: Improvements are modifications or enhancements made to the land or buildings. This can include additions, renovations, or upgrades that increase the value or functionality of the property. Improvements can range from small changes like installing new flooring to significant renovations like adding an additional wing to a building.
Fixtures: Fixtures are items that are attached to the property but can be removed without causing damage. This can include things like light fixtures, ceiling fans, or built-in appliances. Fixtures are typically considered part of the property and are included in the sale unless explicitly excluded in the purchase agreement.
- Land
- Buildings
- Improvements
- Fixtures
- Land
- Buildings
- Improvements
- Fixtures
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Land | The earth’s surface and everything attached to it naturally |
| Buildings | Structures or constructions built on the land |
| Improvements | Modifications or enhancements made to the land or buildings |
| Fixtures | Items attached to the property that can be removed without causing damage |
Understanding the components of real estate is crucial for buyers, sellers, and investors. Each component plays a role in determining the overall value and potential uses of the property.
The Ideal Credit to Debt Ratio for Real Estate
To determine your credit to debt ratio for real estate, you need to know your total monthly debts and your total monthly income. Your debts include things like credit card payments, student loans, car loans, and any other monthly expenses. Your income consists of your salary, rental income, and any other sources of revenue.
Generally, a credit to debt ratio of 36% or lower is considered ideal for real estate purchases. This means that your monthly debts should not exceed 36% of your monthly income. For example, if your total monthly income is $5,000, your total monthly debts should not exceed $1,800. This allows you to have enough disposable income to comfortably afford a mortgage payment, property taxes, and other homeownership expenses.
| Total Monthly Income | Total Monthly Debts | Ideal Credit to Debt Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| $5,000 | $1,800 | 36% |
| $7,000 | $2,520 | 36% |
| $10,000 | $3,600 | 36% |
It’s important to note that while the ideal credit to debt ratio for real estate is 36%, lenders may have different requirements and preferences. Some lenders may be more lenient and accept ratios up to 43%, while others may require a lower ratio of 30% or less. It’s essential to consult with multiple lenders to understand their specific criteria and find the best option for your real estate needs.
How to improve your credit to debt ratio
-
Pay down your debts: Start by paying off high-interest debts first, such as credit card balances. Make larger payments than the minimum required each month to reduce your outstanding debt faster.
-
Reduce your credit card balances: Try to keep your credit card balances below 30% of your available credit limit. Pay off any balances in full each month to avoid interest charges and further reduce your debt.
-
Avoid opening new credit accounts: While it may be tempting to open new credit accounts, doing so can increase your overall debt and negatively affect your credit to debt ratio. Only open new accounts if necessary and manage them responsibly.
-
Monitor your credit report: Regularly check your credit report to ensure it is accurate and dispute any errors you find. Incorrect information on your report can impact your credit to debt ratio and overall creditworthiness.
-
Seek professional help if needed: If you are struggling to manage your debts or improve your credit to debt ratio, consider seeking help from a credit counseling agency. They can provide guidance and assistance in developing a plan to improve your financial situation.
By following these steps, you can work towards improving your credit to debt ratio and ultimately enhance your financial health.
Monitoring your credit to debt ratio

- Regularly check your credit report: It is important to review your credit report at least once a year to ensure its accuracy and identify any potential errors or fraudulent activity. You can request a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus – Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
- Calculate your credit to debt ratio: To calculate your credit to debt ratio, you need to divide your total outstanding debt by your total available credit. For example, if you have a total outstanding debt of $5,000 and a total available credit of $20,000, your credit to debt ratio would be 25%.
- Keep your credit to debt ratio below 30%: It is generally recommended to keep your credit to debt ratio below 30% to maintain a healthy credit score. If your ratio goes above this percentage, it may indicate that you are relying too heavily on credit and may be at risk of defaulting on your payments.
Monitoring your credit to debt ratio is an important aspect of managing your financial well-being. By regularly checking your credit report, calculating your ratio, and keeping it below 30%, you can ensure that you are on track to maintain a healthy credit score and effectively manage your debts.
“Monitoring your credit to debt ratio is crucial for maintaining a healthy financial status and ensuring that you are in control of your debts.”
– Financial Advisor
| Total Outstanding Debt | Total Available Credit | Credit to Debt Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| $5,000 | $20,000 | 25% |
Monitoring your credit-to-debt ratio
Monitoring and maintaining a healthy credit-to-debt ratio is essential for managing your finances and maximizing your chances of securing loans or favorable interest rates. Here is a breakdown of the key components to consider when monitoring your credit-to-debt ratio:
| Component | Description |
| Total Debt | The total amount of debt you owe, including credit card balances, mortgages, and other loans. |
| Total Credit Limit | The maximum amount of credit available to you across all your accounts. |
| Credit Utilization Ratio | The ratio of your total debt to your total credit limit, expressed as a percentage. A lower ratio indicates a lower level of debt compared to your available credit, which is generally viewed more favorably by lenders. |
| Optimal Ratio | An optimal credit-to-debt ratio is generally considered to be below 30%. Higher ratios may negatively impact your credit score and borrowing capacity. |
| Monitoring Tools | Various online platforms and credit monitoring services are available to help you track your credit-to-debt ratio and receive alerts if there are significant changes or potential issues. |
| Benefits | Maintaining a healthy credit-to-debt ratio can improve your credit score, increase your chances of loan approval, and help you qualify for lower interest rates on credit cards, mortgages, and other loans. |
| Actions to Improve Ratio | To improve your credit-to-debt ratio, consider paying down your outstanding balances, increasing your credit limit, and avoiding applying for excessive credit. |
By regularly monitoring your credit-to-debt ratio and taking steps to improve it, you can better manage your overall financial health and achieve your long-term financial goals.
FAQs
What is a credit to debt ratio?
A credit to debt ratio is a financial metric that measures the amount of debt you have compared to the amount of available credit you have.
Why is it important to monitor your credit to debt ratio?
Monitoring your credit to debt ratio is important because it affects your credit score. A higher ratio indicates higher credit utilization, which can negatively impact your credit score and make it harder for you to get approved for loans or credit cards.
How can I calculate my credit to debt ratio?
To calculate your credit to debt ratio, you need to add up all your outstanding debts and divide it by your total available credit. The result is a decimal or a percentage that represents your credit to debt ratio.
What is considered a good credit to debt ratio?
A good credit to debt ratio is typically around 30% or lower. This means that you are using only 30% or less of your available credit. Lenders generally prefer borrowers with lower credit to debt ratios as it shows responsible credit management.
How often should I monitor my credit to debt ratio?
It is recommended to monitor your credit to debt ratio on a regular basis, at least once every few months. This will allow you to spot any significant changes or discrepancies and take necessary actions to improve your financial situation if needed.









